Architecture
Overview
Gloo Gateway aggregates back-end services and provides function-to-function translation for clients, allowing decoupling from back-end APIs. Gloo Gateway sits in the control plane and leverages Envoy to provide the data plane proxy for back-end services.
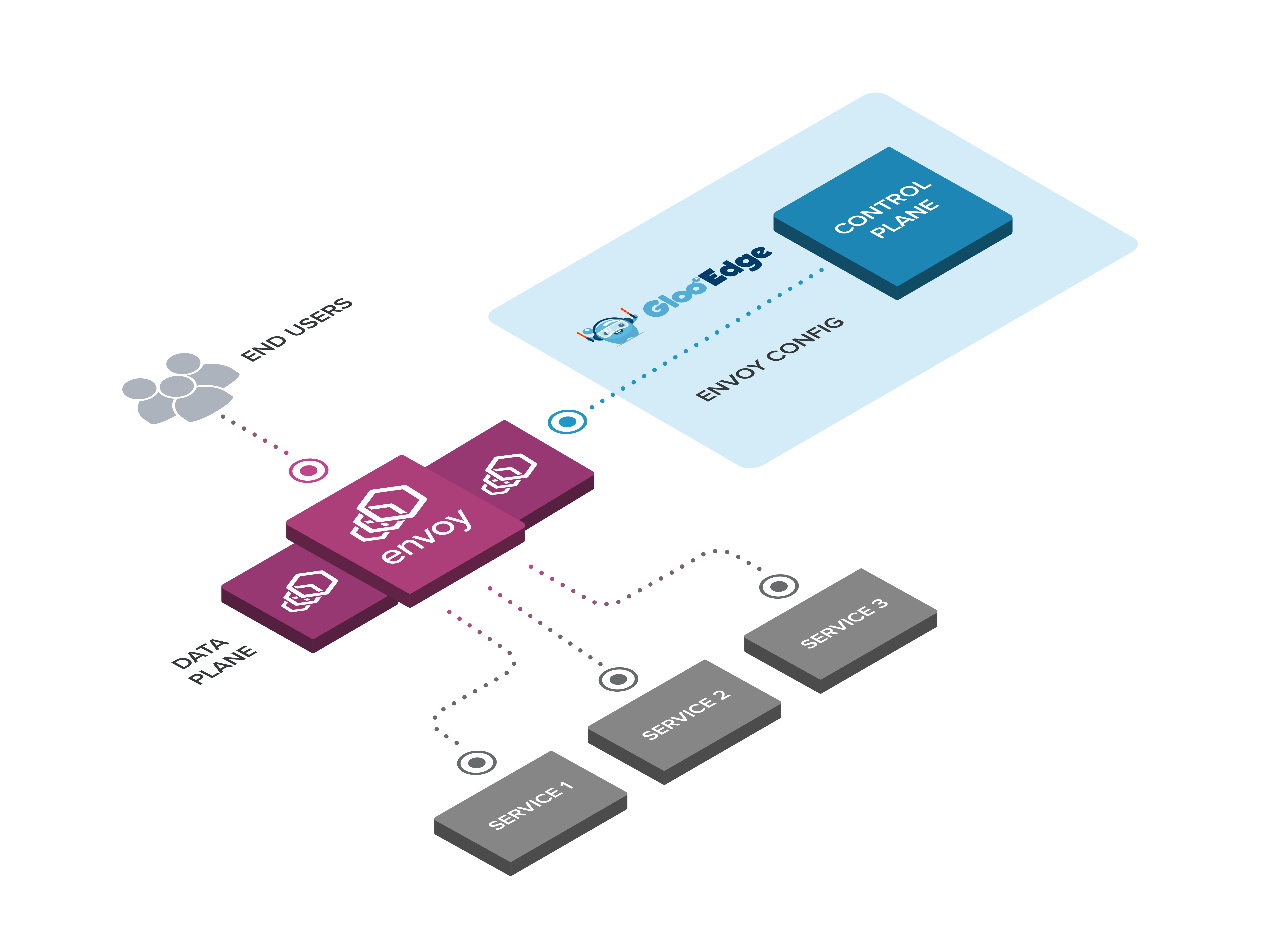
End users issue requests or emit events to routes defined on Gloo Gateway. These routes are mapped to functions on Upstream services by Gloo Gateway’s configuration. The routes are provided by clients through the Gloo Gateway API.
End users connect to Envoy cluster proxies managed by Gloo Gateway, which transform requests into function invocations for a variety of functional back-ends. Non-functional back-ends are supported via a traditional Gateway-to-Service routing model.
Gloo Gateway performs the necessary transformation between the routes defined by clients and the back-end functions. Gloo Gateway is able to support various upstream functions through its extendable function plugin interface.
Gloo Gateway offers first-class API management features on all functions:
- Timeouts
- Metrics & Tracing
- Health Checks
- Retries
- Advanced load balancing
- TLS Termination with SNI Support
- HTTP Header modification
Component Architecture
In the most basic sense, Gloo Gateway is a translation engine and Envoy xDS server providing advanced configuration for Envoy (including Gloo Gateway’s custom Envoy filters). Gloo Gateway follows an event-based architecture, watching various sources of configuration for updates and responding immediately with v2 gRPC updates to Envoy.
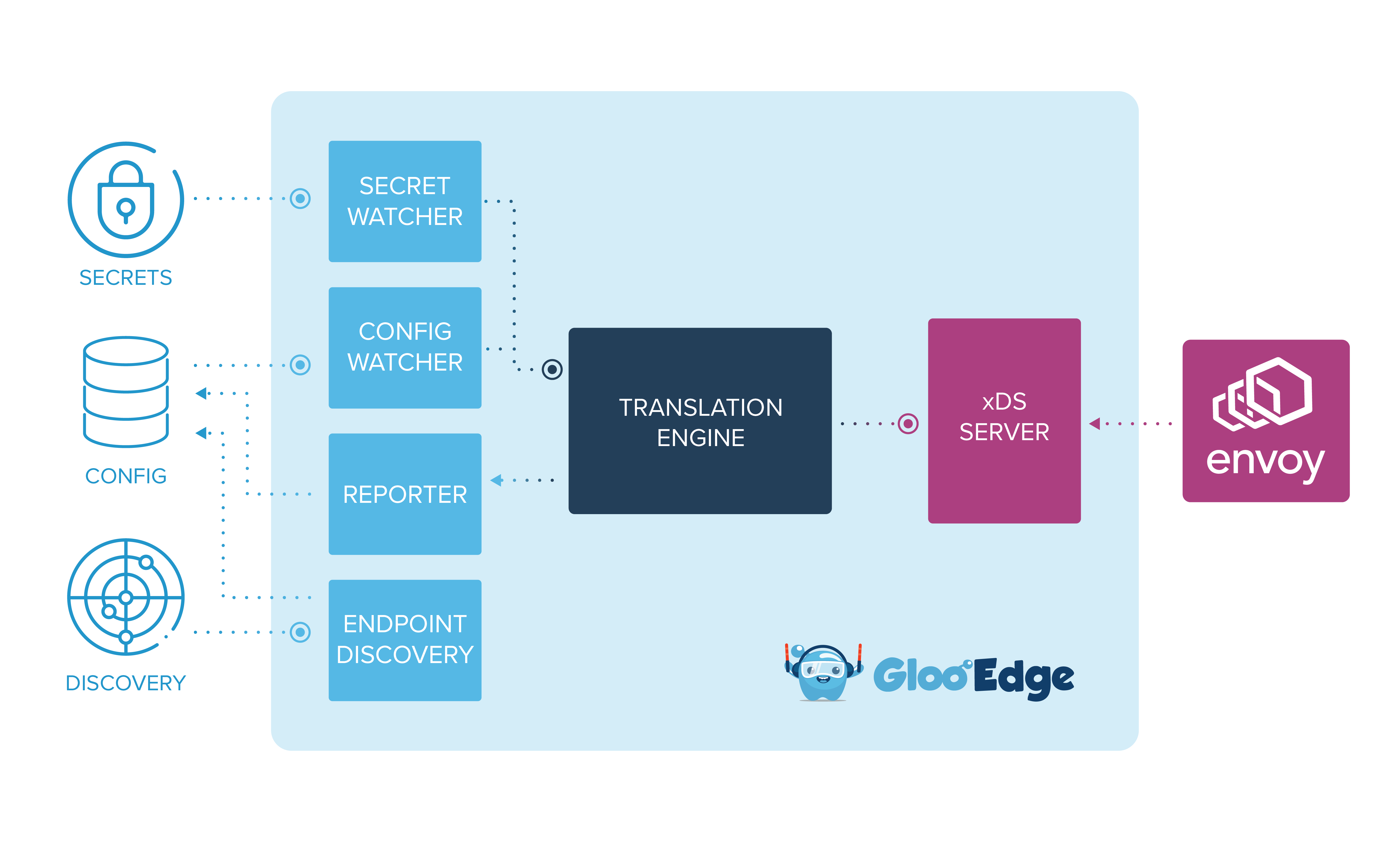
At the logical layer, Gloo Gateway is comprised of several different services that perform unique functions. Gloo Gateway’s control plane sits outside the request path, providing the control layer for Envoy and other services through its transformation plug-in.
The following sections describe the various logical components of Gloo Gateway. The Deployment Architecture guide provides examples and guidance for specific implementations of Gloo Gateway on different software stacks.
Config Watcher
The Config Watcher watches the storage layer for updates to user configuration objects, such as Upstreams and Virtual Services. The storage layer could be a custom resource in Kubernetes or an key/value entry in HashiCorp Consul.
Secret Watcher
The Secret Watcher watches a secret store for updates to secrets (which are required for certain plugins such as the AWS Lambda Plugin . The secret storage could be using secrets management in Kubernetes, HashiCorp Vault, or some other secure secret storage system.
Endpoint Discovery
Endpoint Discovery watches service registries such as Kubernetes, Cloud Foundry, and Consul for IPs associated with services. Endpoint Discovery is plugin-specific, so each endpoint type will require a plug-in that supports the discovery functionality. For example, the Kubernetes Plugin runs its own Endpoint Discovery goroutine.
Gloo Gateway Translator
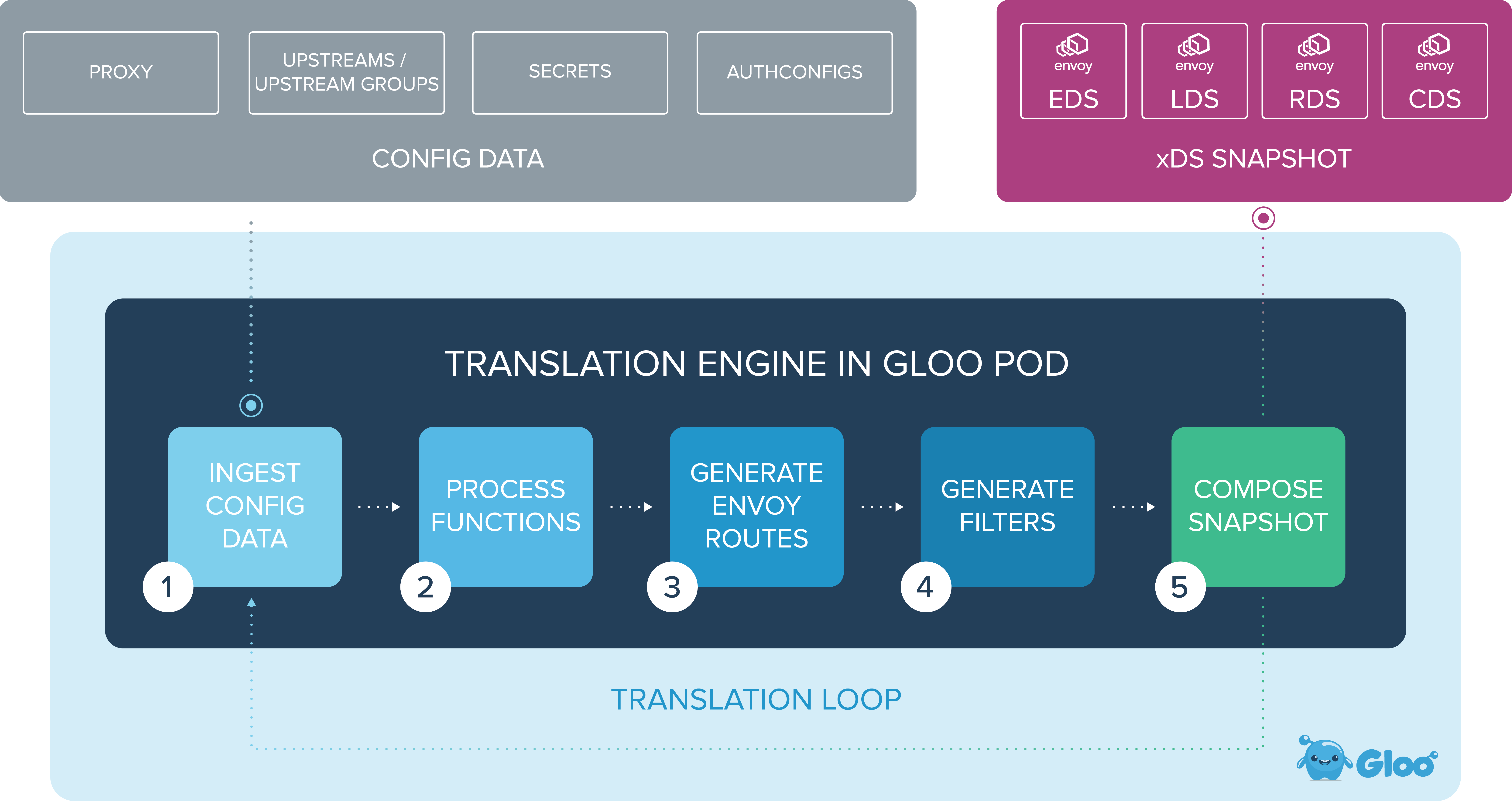
The Gloo Gateway Translator receives snapshots of the entire state, composed of the following configuration data:
- Artifacts
- Endpoints
- Proxies
- Upstreams
- UpstreamGroups
- Secrets
- AuthConfigs
The translator takes all of this information and initiates a new translation loop with the end goal of creating a new Envoy xDS Snapshot.
-
The translation cycle starts by defining Envoy clusters from all configured Upstreams. Clusters in this context are groups of similar Upstream hosts. Each Upstream has a type, which determines how the Upstream is processed. Correctly configured Upstreams are converted into Envoy clusters that match their type, including information like cluster metadata.
-
The next step in the translation cycle is to process all the functions on each Upstream. Function specific cluster metadata is added, which will be later processed by function-specific Envoy filters.
-
The next step generates all of the Envoy routes. Routes are generated for each route rule defined on the Virtual Service objects . When all of the routes are created, the translator aggregates them into Envoy virtual hosts and adds them to a new Envoy HTTP Connection Manager configuration.
-
Filter plugins are queried for their filter configurations, generating the list of HTTP and TCP Filters that will go on the Envoy listeners.
-
Finally, a snapshot is composed of the all the valid endpoints (EDS), clusters (CDS), route configs (RDS), and listeners (LDS). The snapshot will be passed to the xDS Server where Envoy instances watching the xDS server can pull updated snapshots.
Reporter
The Reporter receives a validation report for every Upstream and Virtual Service processed by the translator. Any invalid config objects are reported back to the user through the storage layer. Invalid objects are marked as Rejected with detailed error messages describing mistakes found in the configuration.
xDS Server
The final snapshot is passed to the xDS Server, which notifies Envoy of a successful config update, updating the Envoy cluster with a new configuration to match the desired state set expressed by Gloo Gateway.
Discovery Architecture
Gloo Gateway is supported by a suite of optional discovery services that automatically discover and configure Gloo Gateway with Upstreams and functions to simplify routing for users and self-service.
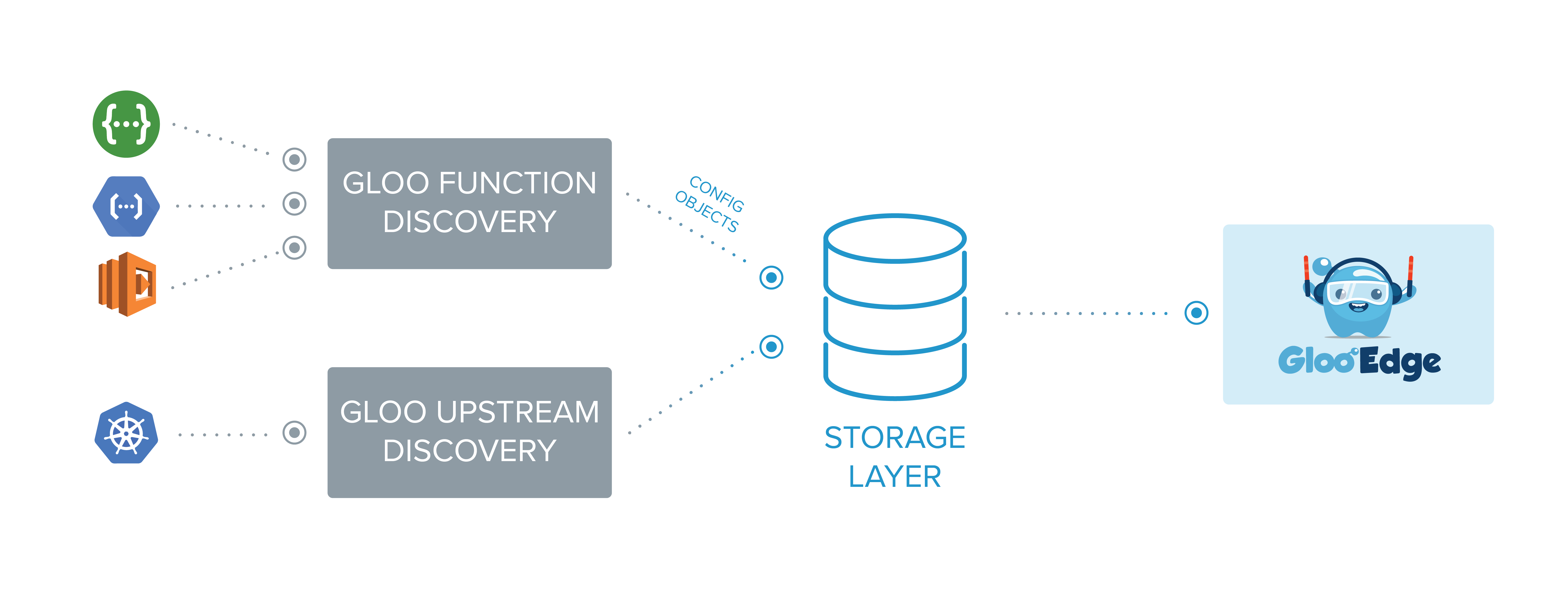
Discovery services act as automated Gloo Gateway clients, automatically populating the storage layer with Upstreams and functions to facilitate easy routing for users. Discovery is optional, but when enabled, it will attempt to discover available Upstreams and functions.
The following discovery methods are currently supported:
- Kubernetes Service-Based Upstream Discovery
- AWS Lambda-Based Function Discovery
- Google Cloud Function-Based Function Discovery
- OpenAPI-Based Function Discovery
Next Steps
Now that you have a basic understanding of the Gloo Gateway architecture, there are number of potential next steps that we’d like to recommend.
- Getting Started: Deploy Gloo Gateway yourself.
- Deployment Architecture: Learn about specific implementations of Gloo Gateway on different software stacks.
- Concepts: Learn more about the core concepts behind Gloo Gateway and how they interact.
- Developer Guides: extend Gloo Gateway’s functionality for your use case through various plugins.
